The Power of Innovation: Exploring the 831b Phenomenon
Innovation has always been a driving force behind progress, propelling industries towards new horizons and opening doors to unforeseen possibilities. One such phenomenon that has garnered significant attention in recent years is the 831b captive insurance arrangement. This unique approach, enabled by the IRS 831b tax code provision, has revolutionized the way small businesses and individuals manage their risks.
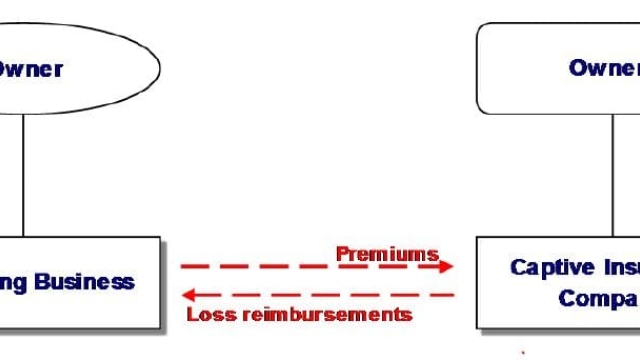
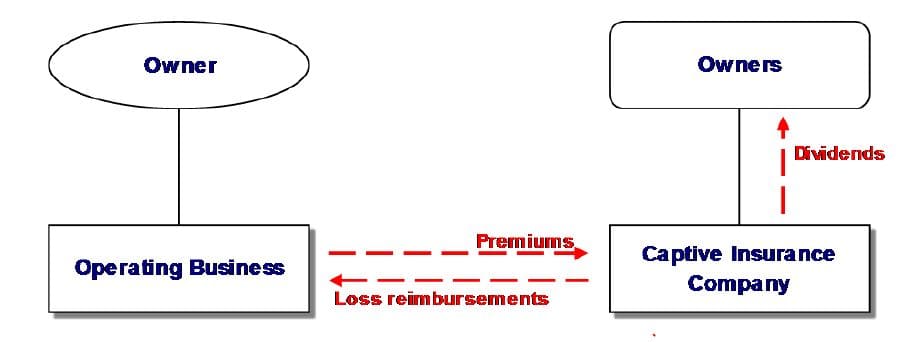
At its core, the 831b phenomenon revolves around the concept of microcaptives, which are small insurance companies primarily formed to provide coverage for the risks of their owners. By taking advantage of the 831b tax code provision, these microcaptives can benefit from certain tax advantages that make them an attractive alternative to traditional insurance methods. This innovative approach allows businesses and individuals to take greater control over their risk management strategies, tailor insurance policies to their specific needs, and potentially achieve significant tax savings in the process.
As we delve into the realm of the 831b phenomenon, we will explore the intricacies of captive insurance arrangements and discover the various advantages and considerations that come with this innovative approach. From understanding the eligibility requirements set forth by the IRS to discerning the potential risks and rewards, we will examine how 831b captives have opened up a world of possibilities for businesses seeking comprehensive risk management solutions. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the power of innovation embodied in the 831b phenomenon.
Understanding the 831b Tax Code
The 831b tax code refers to a specific provision in the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regulations that outlines the rules and regulations surrounding captive insurance companies, often referred to as microcaptives. This tax code section provides certain tax advantages and incentives for small insurance companies that meet the requirements set forth by the IRS.
Under the 831b tax code, a captive insurance company is defined as a company formed to provide insurance coverage to its parent company or affiliated companies. These captive insurers typically insure risks that are not adequately covered by traditional insurance companies. By doing so, they help their parent companies manage and mitigate potential risks, while also potentially realizing tax benefits.
In order to qualify for the advantages provided by the 831b tax code, a microcaptive must meet certain criteria, such as limiting its net premium income and having a specific diversification of risk. The IRS requires that the insurance premiums received by the microcaptive be less than $2.3 million per year, making this provision primarily applicable to smaller insurance companies.
By utilizing the 831b tax code, eligible captive insurance companies can potentially benefit from a reduced tax rate on their underwriting income. This tax advantage has made microcaptives an attractive option for certain businesses, providing them with the opportunity to not only enhance their risk management strategies but also potentially decrease their tax liability.
In conclusion, the 831b tax code plays a crucial role in enabling small insurance companies to establish captive insurance arrangements and potentially realize tax advantages. Understanding the provisions and requirements outlined in this tax code section is essential for those considering utilizing this innovative approach to risk management and tax planning.
Exploring the Benefits of Captive Insurance
Captive insurance, often referred to as 831b in relation to the specific section of the IRS tax code, has gained significant traction in recent years as a powerful tool for managing risks and maximizing financial benefits. This innovative approach to insurance allows businesses to establish their own insurance company, known as a "microcaptive," to cover their unique risks that are often not adequately addressed by traditional insurance providers.
One of the main advantages of captive insurance is the increased control and flexibility it offers to businesses. With a captive insurance arrangement, companies can tailor their insurance coverage to specifically meet their needs, rather than relying on generic policies offered by third-party insurers. This enables businesses to protect themselves against risks that are not adequately covered in the market or to create coverage for risks that are not typically insurable.
Additionally, captive insurance can provide significant financial benefits to businesses. Through the establishment of a captive insurance company, businesses can retain a portion of the premiums they pay, creating an opportunity for potential cost savings and enhanced cash flow. This retained capital within the captive can be invested and generate returns, further strengthening the overall financial position of the businesses.
Furthermore, captive insurance can serve as an effective risk management tool. By carefully analyzing and addressing their unique risks, businesses can take proactive measures to minimize losses and protect their assets. Rather than solely relying on the uncertainties of the commercial insurance market, captive insurance empowers businesses to be in the driver’s seat when it comes to managing their risks.
In summary, captive insurance, commonly known as 831b, offers a range of benefits to businesses looking for a tailored and flexible approach to insurance. By establishing their own insurance company, businesses can gain control, customization, and potential cost savings while effectively managing their risks. This phenomenon is revolutionizing the insurance landscape and opening up new opportunities for businesses to navigate their risk landscape with confidence.
The Rise of Microcaptives
The growing popularity of 831b microcaptives has given birth to a significant trend in the insurance industry. As businesses strive to find innovative ways to manage risk and reduce their tax obligations, more and more companies are turning to captives as a viable solution.
In the past, captive insurance arrangements were predominantly utilized by larger corporations with substantial resources. However, with the introduction of the 831b tax code by the IRS, smaller businesses can now take advantage of these microcaptives. This shift has opened up new opportunities for entrepreneurs and small to mid-sized companies alike.
The attractiveness of microcaptives lies in their ability to provide significant benefits such as greater control over the insurance claims process, enhanced risk management, and potential tax advantages. By establishing their own captive insurance company, businesses gain the flexibility to tailor coverage options specific to their needs, ensuring comprehensive protection against various risks.
It’s important to acknowledge that the rise of microcaptives has not been without controversy. Some have raised concerns about potential abuse of the 831b tax code, leading to increased scrutiny by regulatory authorities. However, many legitimate businesses recognize the genuine advantages that microcaptives offer and are utilizing them responsibly.
In summary, the surge in popularity of microcaptives represents a notable shift in the insurance landscape. With the 831b tax code providing a pathway for smaller businesses to establish captive insurance arrangements, entrepreneurs now have access to the same risk management strategies previously reserved for larger corporations. As businesses continue to explore the power of innovation, it will be interesting to see how this phenomenon evolves and shapes the future of the insurance industry.