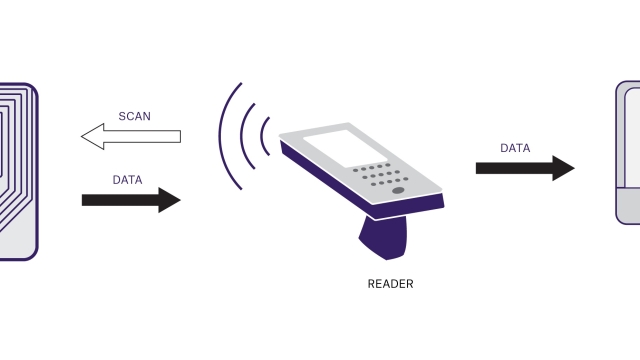
The Future Unleashed: Exploring the Power of RFID Technology
RFID technology has emerged as a transformative force in a rapidly advancing world. With its ability to wirelessly identify and track objects, this technology is poised to revolutionize numerous industries, from retail to logistics, healthcare to manufacturing. The Future Unleashed: Exploring the Power of RFID Technology delves deep into the endless possibilities that this innovative technology holds.
At its core, RFID, which stands for Radio Frequency Identification, enables the seamless exchange of data between objects and systems. It empowers organizations to streamline their operations, enhance supply chain visibility, and capture valuable insights in real-time. By employing tiny electronic tags, RFID eliminates the need for manual scanning, providing a swift and accurate means of identifying objects and assets. This technology empowers businesses to unlock unprecedented efficiency, optimize inventory management, and enhance customer experiences. The power of RFID lies not just in its ability to track physical objects, but also in its potential to transform entire ecosystems for the better.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of RFID technology, we will explore its underlying principles, examine its implementation across various domains, and delve into the promising future it brings. By understanding the capabilities and potential of RFID technology, we can truly grasp how it is shaping the landscapes of tomorrow, and how it will continue to unlock new opportunities across industries. The future of RFID is indeed thrilling, and this article aims to unravel its power and significance in an increasingly interconnected world.
Applications of RFID Technology
RFID technology has found widespread application in various industries and sectors. Its versatility and efficiency have revolutionized many processes, bringing about significant advancements and improvements. Let’s explore some key areas where RFID technology is being utilized.
- Supply Chain Management:
RFID technology is extensively used in supply chain management to enhance visibility and streamline operations. With RFID tags attached to products, shipments can be easily tracked and monitored at every stage of the supply chain. This enables real-time inventory management, reducing the chances of stockouts and ensuring efficient replenishment.
- Retail:
In the retail industry, RFID technology has paved the way for faster and more accurate inventory management. By tagging individual items with RFID tags, retailers can perform quick and automated stock checks, eliminating the need for manual scanning. This not only saves time but also enhances the overall shopping experience by reducing checkout delays and improving stock availability.
- Healthcare:
In the healthcare sector, RFID technology is proving invaluable for patient monitoring, asset tracking, and medication management. RFID tags on patient wristbands enable healthcare professionals to accurately identify and track patients, ensuring the right treatments are administered to the right individuals. Additionally, RFID tags can help track and manage valuable medical equipment and supplies, improving resource allocation and reducing costs.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of RFID technology. From logistics to retail and healthcare, the potential for harnessing RFID technology is vast, promising increased efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in various domains.
Advantages of RFID Technology
RFID technology offers numerous advantages, revolutionizing various industries and enhancing efficiency in numerous applications.
-
Enhanced Inventory Management: With RFID technology, tracking and managing inventory becomes a seamless task. RFID tags can be easily attached to products, allowing for real-time monitoring and accurate stock levels. This not only reduces human error but also enables businesses to streamline their supply chain operations and optimize inventory control.
-
Improved Operational Efficiency: The use of RFID technology can significantly improve operational efficiency across various sectors. By automating processes such as asset tracking, shipment verification, and document management, RFID eliminates the need for manual intervention, reducing time-consuming tasks and increasing productivity.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: RFID technology enables a more personalized and seamless customer experience. By integrating RFID tags into products or implementing RFID-enabled access control systems, businesses can offer convenient self-checkout options, personalized recommendations, and streamlined access to services. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also fosters brand loyalty and generates valuable insights for targeted marketing strategies.
In conclusion, RFID technology provides substantial advantages in inventory management, operational efficiency, and customer experience. Its ability to automate processes, increase accuracy, and improve overall productivity makes it an invaluable tool for businesses across various industries. The future of RFID technology looks promising, promising to continue revolutionizing the way we interact with our surroundings.
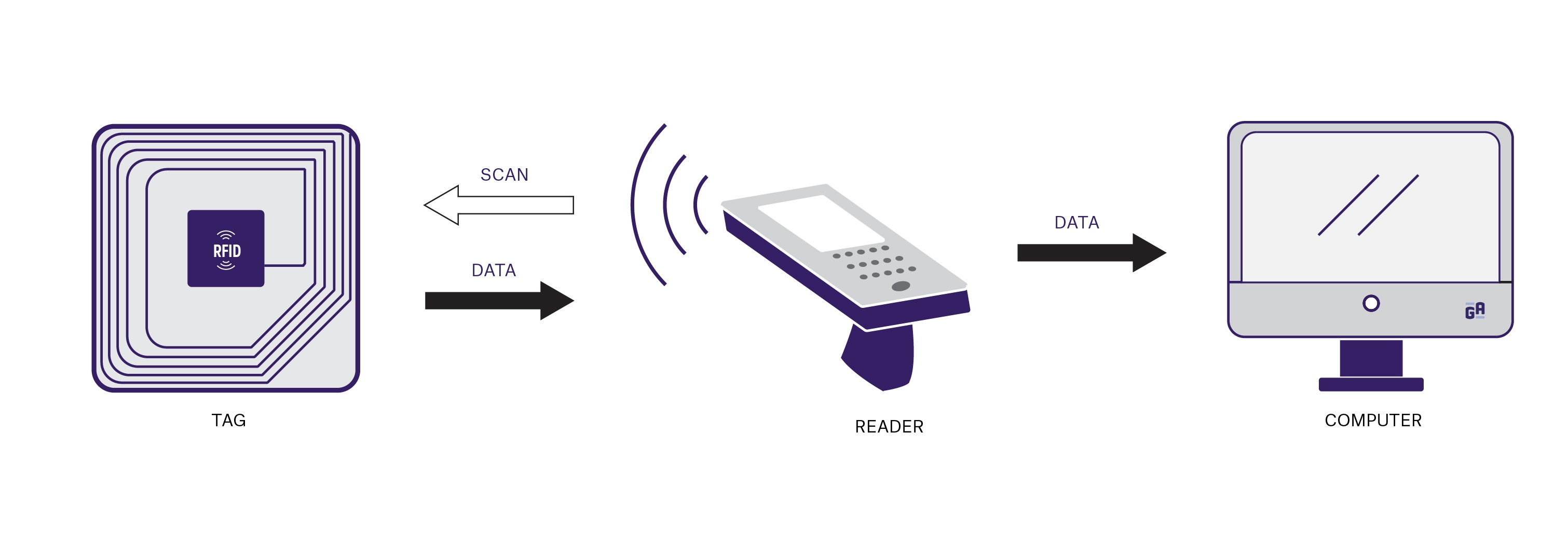
Challenges and Limitations of RFID Technology
RFID technology, while promising and powerful, also faces certain challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for its wider adoption and effective implementation.
Firstly, one of the primary challenges is the issue of range and read accuracy. RFID systems rely on radio frequency signals to communicate between the tags and readers. However, the effectiveness of the communication can be hindered by various environmental factors such as interference from other electronic devices, metal objects, and even physical barriers like walls or doors. This can result in reduced read accuracy or limited range, making it necessary to optimize the placement of readers and tags to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
Secondly, privacy concerns pose a significant limitation to the widespread acceptance of RFID technology. The ability of RFID tags to uniquely identify objects or individuals raises concerns about potential misuse or unauthorized tracking. For instance, in applications such as supply chain management or access control, the collection and storage of RFID data may raise privacy issues if not properly protected. Striking a balance between the benefits of RFID technology and the protection of individual privacy rights is a key challenge that needs to be addressed through robust security measures and regulations.
Lastly, cost and scalability are additional challenges faced by RFID technology. Although the cost of RFID tags and readers has decreased over the years, it still remains a considerable investment, especially for large-scale deployments. Additionally, integrating RFID systems into existing infrastructure or supply chain processes can be complex and require significant resources. Hence, cost-effectiveness and scalability remain important factors in determining the practicality and feasibility of RFID implementation across various industries.
In conclusion, while RFID technology offers great promises in terms of efficiency and tracking capabilities, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the challenges and limitations it faces. Overcoming issues of range and read accuracy, ensuring privacy protection, and improving cost-effectiveness and scalability will ultimately contribute to unlocking the full potential of RFID technology and fuel its future advancements.